Non-metallic enclosures are specially designed protective cases used in electrical applications to house sensitive equipment and components. Unlike traditional metal enclosures, these industrial enclosures are made from materials such as fiberglass, polycarbonate, or ABS, offering various advantages in terms of durability, weather resistance, and versatility.
Benefits of Non-Metallic Enclosures
• Non-metallic enclosures provide several benefits that make them preferable in many industries. These advantages include:
• Corrosion Resistance: Non-metallic enclosures are highly resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for outdoor or corrosive environments.
• Lightweight and Easy to Install: Compared to metal enclosures, non-metallic enclosures are lightweight and easy to handle, reducing installation time and effort.
• Electrical Insulation: Non-metallic materials offer excellent electrical insulation, ensuring safety and preventing electrical hazards.
• UV Resistance: Non-metallic enclosures can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight without degrading, making them ideal for outdoor applications.
• Chemical Resistance: Many non-metallic enclosures have superior chemical resistance, protecting the enclosed equipment from harmful substances.
Non-Metallic Enclosures vs. Metal
Non-metallic enclosures offer several size and cost advantages compared to their metallic counterparts. Here are some of the key benefits:
Lightweight: Non-metallic enclosures are generally much lighter than metal enclosures. This lightweight nature makes them easier to handle, transport, and install, reducing labor and transportation costs.
Corrosion Resistance: Unlike metal enclosures, non-metallic enclosures are typically corrosion-resistant. They can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation, without deteriorating. This corrosion resistance reduces the need for frequent maintenance or replacement, resulting in cost savings over time.
Cost-effective Materials: Non-metallic enclosures are often made from cost-effective materials such as thermoplastics, fiberglass, or composites. These materials are generally less expensive than metals like stainless steel or aluminum, making non-metallic enclosures more affordable.
Design Flexibility: Non-metallic enclosures offer greater design flexibility compared to metal enclosures. They can be molded or formed into various shapes and sizes. They are also easy to modify by machining or cutting, allowing customization to meet specific application requirements. This flexibility can save costs by eliminating difficult adaptations.
Electrical Insulation: Non-metallic enclosures provide excellent electrical insulation properties. They are non-conductive and can effectively isolate electrical components from external factors, reducing the risk of electrical shocks and equipment damage. This insulation property can contribute to overall safety and reliability while reducing the need for additional insulation materials, thus lowering TCO costs and increasing safety.
Ease of Modification: Non-metallic enclosures can be easily modified or adapted without specialized tools or techniques. They can be drilled, cut, or molded on-site, allowing quick and convenient adjustments during installation or future equipment upgrades. This ease of modification reduces labor costs and enhances installation efficiency.
Full-Featured Non-Metallic Enclosure:

Non-Metallic Enclosure types and their specific advantages over one another
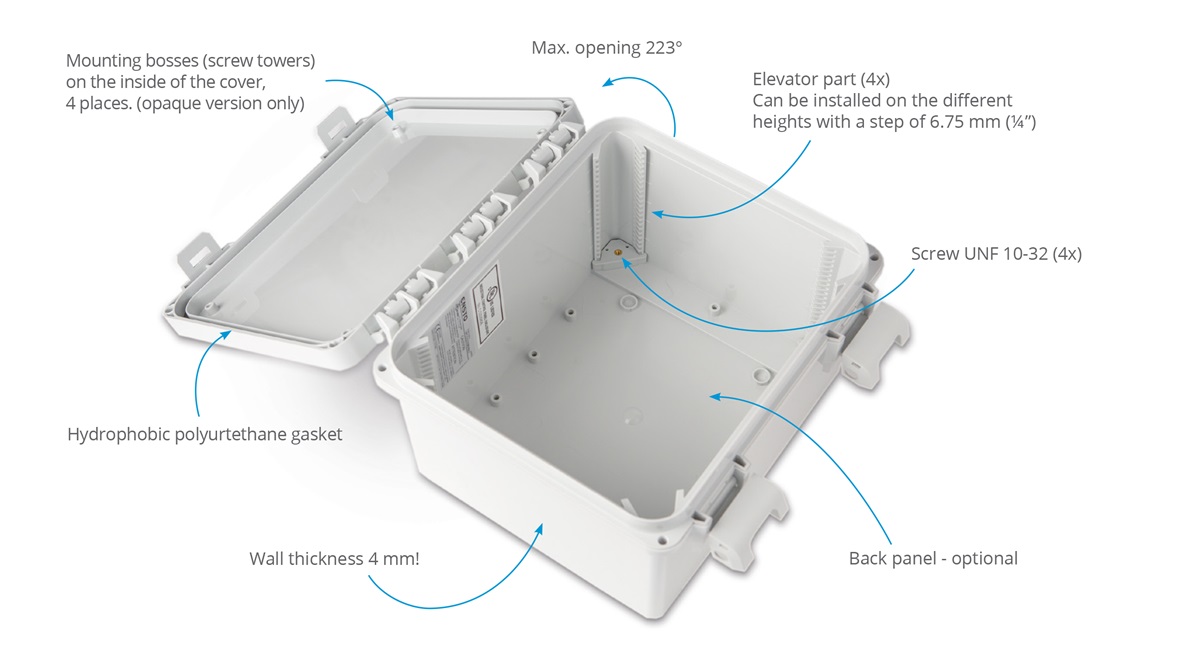
Polycarbonate Enclosures
Advantages
Polycarbonate enclosures are known for their excellent impact resistance, allowing for thinner walls without compromising strength. This characteristic makes designing compact and lightweight enclosures possible while providing adequate protection for the enclosed equipment. Modern Polycarbonate enclosures usually contain a UV stabilizer to protect and prolong outdoor UV exposure. These PC enclosures are comparable, if not better, than fiberglass.
Cost
Polycarbonate enclosures are relatively cost-effective due to their high impact resistance and durability. They offer a long service life, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance, which can contribute to overall cost savings.
Concerns
Scratching and Wear: Polycarbonate is relatively softer than materials like glass or metal, making it more prone to scratching. In high-traffic or abrasive environments, the surface of the polycarbonate enclosure may show signs of wear, impacting its appearance or transparency (like a clear door).
Temperature Limitations: Polycarbonate has temperature limitations. It can deform or soften when exposed to high temperatures, compromising its structural integrity. Alternative materials with better heat resistance may be more suitable for elevated temperatures or thermal cycling applications.
Chemical Sensitivity: Polycarbonate can be sensitive to certain chemicals, solvents, or cleaning agents. Exposure to incompatible chemicals may cause discoloration, surface damage, or weakening of the enclosure. It's important to ensure that any chemicals used in the vicinity of polycarbonate enclosures are compatible with the material.

Fiberglass Enclosures
Advantages
Fiberglass enclosures can be manufactured in various sizes and shapes, offering flexibility for accommodating different equipment and components. They can be designed to fit specific requirements, including large or unusually shaped equipment.
Cost
Fiberglass enclosures can be more expensive than other materials commonly used in industrial enclosures, such as steel or plastics. Fiberglass enclosures are generally cost-effective for "larger" sizes. When comparing this material cost to other non-metallic enclosures, fiberglass enclosure size-to-price advantage typically happens above the 12" x 12" size. Fiberglass becomes a very economical choice above this size, and this is due to the other materials' production waste and molding costs.
Concerns
Fragility: Despite its overall strength, fiberglass can be relatively brittle and prone to cracking or breaking upon impact or exposure to excessive force. This can lead to the need for frequent repairs or replacement of enclosures, increasing maintenance costs.
Weight: Fiberglass enclosures are heavier than alternatives such as plastics or metals. This can make transportation and installation more challenging, requiring additional equipment and labor.
Limited Temperature Resistance: Fiberglass may have limitations in its ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It can warp or degrade in high-temperature environments, compromising its structural integrity.

Polyester Enclosures
Advantages
Polyester enclosures provide excellent resistance to chemicals, making them suitable for harsh environments. They can be manufactured in various sizes, allowing flexibility in accommodating different equipment and components. Polyester is recyclable.
Cost
Polyester enclosures offer good value for their cost. While they may be slightly more expensive than some other non-metallic options, their durability and resistance to chemicals can result in long-term cost savings by minimizing maintenance and replacement needs.
Concerns
Chemical Additives: Polyester enclosures may contain chemical additives, such as plasticizers, flame retardants, or UV stabilizers. These additives can leach out over time, posing risks to human health and the environment. Care should be taken to ensure the use of safe and non-toxic additives.
Durability: While polyester enclosures are generally durable, they may be susceptible to degradation and fading when exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, UV radiation, or chemicals. Regular maintenance and protective coatings may be required to maintain their integrity.

ABS Enclosures
Advantages
ABS enclosures are available in various sizes and shapes, providing flexibility for multiple applications. They can be easily molded into complex forms, allowing customization to meet specific equipment or component requirements.
Cost Advantages
ABS is known for its cost-effectiveness. It is a relatively inexpensive material, making ABS enclosures an affordable option. The low manufacturing costs associated with ABS contribute to their overall cost advantage.
Concerns
Environmental: ABS is not biodegradable, and if improperly disposed of, it can persist in the environment for a long time, adding to plastic waste accumulation. These resins have been controversial in recent years: leaching is the basis of this controversy. Leaching occurs at high temperatures and releases bisphenol A, a compound on the list of potential environmental hazardous chemicals. Moreover, the decomposition of BPA in landfills does not occur, meaning that this chemical will persist in the ground and eventually find its way into water bodies contributing to aquatic pollution. This type of plastic cannot be recycled.
Limited Temperature Resistance: ABS has relatively lower heat resistance than other materials, such as metals. It can deform or soften when exposed to high temperatures, which may limit its suitability for applications that involve elevated temperatures or thermal cycling.
Impact Resistance: While ABS is generally known for its impact resistance, it may not be as durable as other materials, such as fiberglass or metal. There is a higher risk of cracking or damage when the enclosure is exposed to frequent impacts or heavy mechanical stress.
Chemical Resistance: ABS may not be highly resistant to certain chemicals or solvents. It can be susceptible to chemical attack, leading to surface degradation or weakening of the enclosure. Care should be taken to assess the compatibility of ABS with specific chemicals in the operating environment.
UV Degradation: When exposed to prolonged sunlight or ultraviolet (UV) radiation, ABS can undergo degradation. It may experience color fading, surface discoloration, or reduced mechanical properties.
Flammability: ABS is a combustible material and can burn when exposed to fire or high heat. It releases potentially toxic smoke and gases when it burns, posing risks to occupants and sensitive equipment.

PVC Enclosures
Advantages
PVC enclosures can be manufactured in different sizes and shapes to accommodate various equipment and components. They offer good dimensional stability and can maintain shape under tough environmental conditions.
Cost Advantages
PVC is a cost-effective material for enclosures. It is generally less expensive than other non-metallic options, making PVC enclosures a cost-efficient choice. PVC is widely available, contributing to its affordability.
Concerns
Environment: PVC is not easily biodegradable and can persist in the environment for a long time if improperly disposed of. This plastic type was the world's second most widely used plastic resin (after polyethylene). PVC has been proven toxic to dispose of and known to cause serious health risks and environmental pollution issues. PVC is considered the most hazardous plastic. The use of it may leach a variety of toxic chemicals such as bisphenol A (BPA), phthalates, lead, dioxins, mercury, and cadmium.
Chemical Emissions: PVC enclosures can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other chemicals, particularly when exposed to heat or certain solvents. These emissions can negatively impact indoor air quality, posing potential health risks to occupants or sensitive equipment. Proper ventilation and adequate off-gassing time should be considered after installation.
Temperature Limitations: PVC enclosures have temperature limitations, particularly in high-temperature environments. PVC can soften or deform when exposed to excessive heat, potentially compromising its structural integrity. This restricts its suitability for applications that involve elevated temperatures or thermal cycling.
Impact Resistance: While PVC is generally impact-resistant, it may not be as durable as other materials, such as fiberglass or metal. There is a higher risk of cracking or damage when the enclosure is subject to frequent impacts or heavy mechanical stress.
UV Degradation: Unprotected PVC is susceptible to degradation when exposed to prolonged sunlight or UV radiation. It can experience color fading, embrittlement, or surface discoloration over time.
Fire Hazard: PVC is a combustible material and can release toxic gases and smoke when exposed to fire. It may contribute to the spread and intensity of a fire. Fire safety measures, such as using flame-retardant additives or implementing fire suppression systems, should be considered when using PVC enclosures.
Cost: PVC enclosures can be cost-effective compared to certain alternatives, such as metal, but they are not necessarily less expensive than other non-metallic enclosures. Their price will vary depending on the size, design complexity, and specific requirements of the project.

Polystyrene Enclosure
Advantages
Polystyrene enclosures can be manufactured in various sizes and shapes to accommodate different equipment and components. They are versatile and can be molded into complex forms, allowing customization based on specific application requirements.
Cost Advantages
Polystyrene is generally a cost-effective material. It is inexpensive compared to other non-metallic options, making polystyrene enclosures affordable. The low cost of manufacturing polystyrene contributes to its cost advantage. However, their price may vary depending on factors such as the thickness and quality of the material and design complexity.
Concerns
Environmental: It's among the worst types of plastic: it is not biodegradable. Due to their low specific gravity, polystyrene microplastics can become airborne and float on water. Animals do not recognize it as artificial and may mistake it for food causing serious effects on the health of birds or marine animals that might swallow it. Which later become ingested by humans. These materials persist in the environment for a long time, contributing to plastic waste accumulation.
Fragility: Polystyrene is relatively brittle, making it more prone to cracking or breaking under impact or excessive force. This fragility can limit its durability and require careful handling and protection during transportation and installation.
Limited Temperature Resistance: Polystyrene has lower heat resistance compared to other materials. It can soften or deform when exposed to high temperatures, potentially compromising the enclosure's structural integrity. It is not suitable for applications involving elevated temperatures.
Chemical Sensitivity: Polystyrene can be sensitive to certain chemicals, solvents, or cleaning agents. Exposure to incompatible substances may cause surface damage, discoloration, or weakening of the enclosure. It's important to ensure that any chemicals used in the vicinity of polystyrene enclosures are compatible with the material.
Flammability: Polystyrene is a flammable material and can easily ignite when exposed to fire or high heat. It releases toxic gases and smoke when it burns, posing risks to occupants and sensitive equipment. Fire safety measures, such as using flame-retardant additives or implementing fire suppression systems, should be considered when using polystyrene enclosures.
Durability: Compared to other non-metallic materials, polystyrene enclosures have limitations in terms of long-term durability. They may be more susceptible to weathering, UV degradation, and physical damage, requiring regular maintenance or replacement.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Non-Metallic Enclosures
When selecting a non-metallic enclosure, consider the following factors:
• Durability: Ensure the enclosure can withstand the environmental conditions it will be exposed to, such as extreme temperatures, moisture, or chemicals.
• Size and Configuration: Select an enclosure that accommodates your equipment's size and configuration requirements, allowing sufficient space for installation and maintenance.
• Certification and Compliance: Check if the enclosure meets relevant industry standards and certifications for safety and performance.
• Customization Options: Consider whether customization options such as cutouts, windows, or mounting accessories are available to meet specific application needs.
Installation and Maintenance of Non-Metallic Enclosures
• Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for maximizing the benefits of non-metallic enclosures. Follow these steps:
• Pre-Installation Preparation: Read the manufacturer's instructions and ensure you have all the necessary tools and equipment.
• Mounting and Securing: Position the enclosure securely, ensuring proper alignment with the equipment. Use appropriate mounting hardware to secure it.
• Cable Entry and Sealing: Pay attention to cable entry points and seal them properly to maintain the enclosure's IP rating and prevent moisture ingress.
• Regular Inspection and Cleaning: Periodically inspect the enclosure for any signs of damage or wear. Clean the enclosure using non-abrasive materials to remove dust or debris.
• Component Compatibility: Ensure that any components or accessories added to the enclosure are compatible and do not compromise its performance or integrity.
TLDR;
Non-metallic enclosures offer an excellent alternative to traditional metal enclosures in electrical applications. Their durability, weather resistance, and versatility make them ideal for various industries. Considering factors like durability, size, and customization options, you can choose the right non-metallic enclosure that meets your requirements. Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for ensuring your equipment's long-term performance and protection.
Need help?
We're here to support your design and engineering needs.
You can get expert assistance now.