Energy monitoring has always been integral to managing and optimizing energy usage for businesses and industries. However, with the advent of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), energy monitoring has become more advanced, efficient, and effective. The IIoT has revolutionized many industries, including energy, by providing real-time data and insights that were previously inaccessible. In this blog, we will explore how IIoT is transforming energy monitoring, the benefits of IIoT, the challenges of implementing it, and the future of IIoT in energy monitoring.
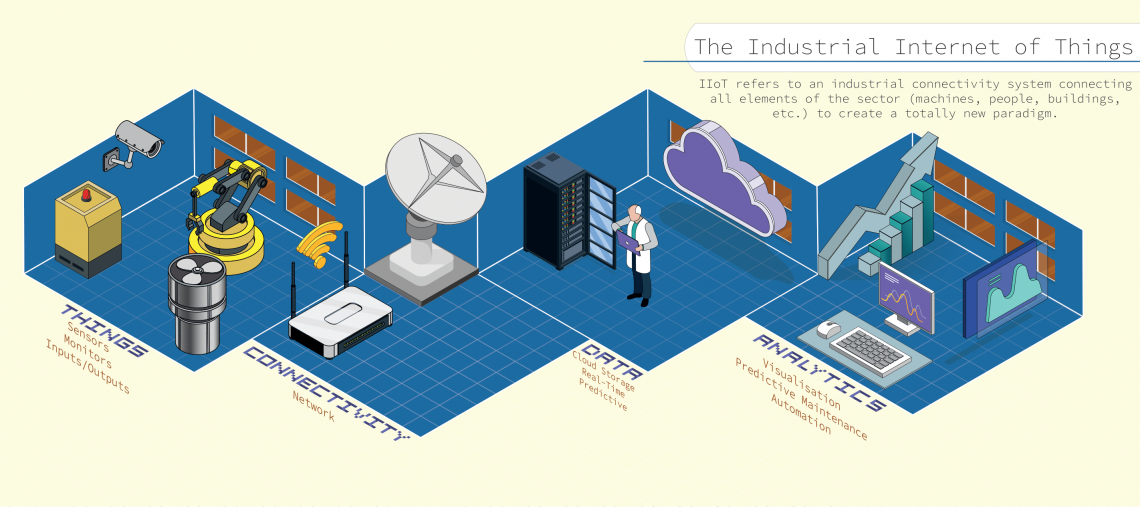
Introduction to IIoT and energy monitoring
The IIoT is a network of connected devices, machines, sensors, and software that communicate and share data over the internet. The IIoT has transformed industrial systems, providing real-time data and advanced analytics for better decision-making. Energy monitoring is a critical component of the IIoT, enabling businesses to track and optimize their energy usage, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
Energy monitoring involves tracking energy consumption and identifying waste areas, which can be costly for businesses. In addition, traditional energy monitoring systems rely on manual data collection and analysis, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. However, with IIoT, energy monitoring has become more automated, accurate, and efficient.
The traditional approach to energy monitoring
The traditional approach to energy monitoring involves manual data collection and analysis. This method is time-consuming and can lead to errors due to the human factor. Traditional energy monitoring systems typically include using meters to measure energy consumption and collecting data at regular intervals, then analyzing the data manually to identify areas of waste and inefficiency.
This approach is efficient and can also be costly for businesses. With real-time data and insights, companies can make informed decisions about their energy usage, leading to wastage and higher costs.
The benefits of IIoT in energy monitoring
The IIoT has transformed energy monitoring, providing real-time data and insights that were previously unavailable.
One of the significant benefits of IIoT in energy monitoring is improved energy efficiency. By analyzing data from various sources, IIoT devices can identify energy-saving opportunities, which can help reduce energy consumption and costs. Additionally, IIoT devices can enable predictive maintenance, which helps identify potential equipment failures before they occur, avoiding costly downtime and repairs.
Another significant benefit of IIoT in energy monitoring is improved sustainability. By monitoring energy consumption in real-time, businesses can identify areas to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint. Keeping track of energy consumption helps achieve sustainability goals and reduces a company's environmental impact.
IIoT devices also provide businesses with greater visibility into their energy consumption patterns. By analyzing data from various sources, companies can gain insights into their energy usage patterns and identify improvement areas. Proper energy analysis helps make informed decisions about energy consumption and planning for future energy needs.
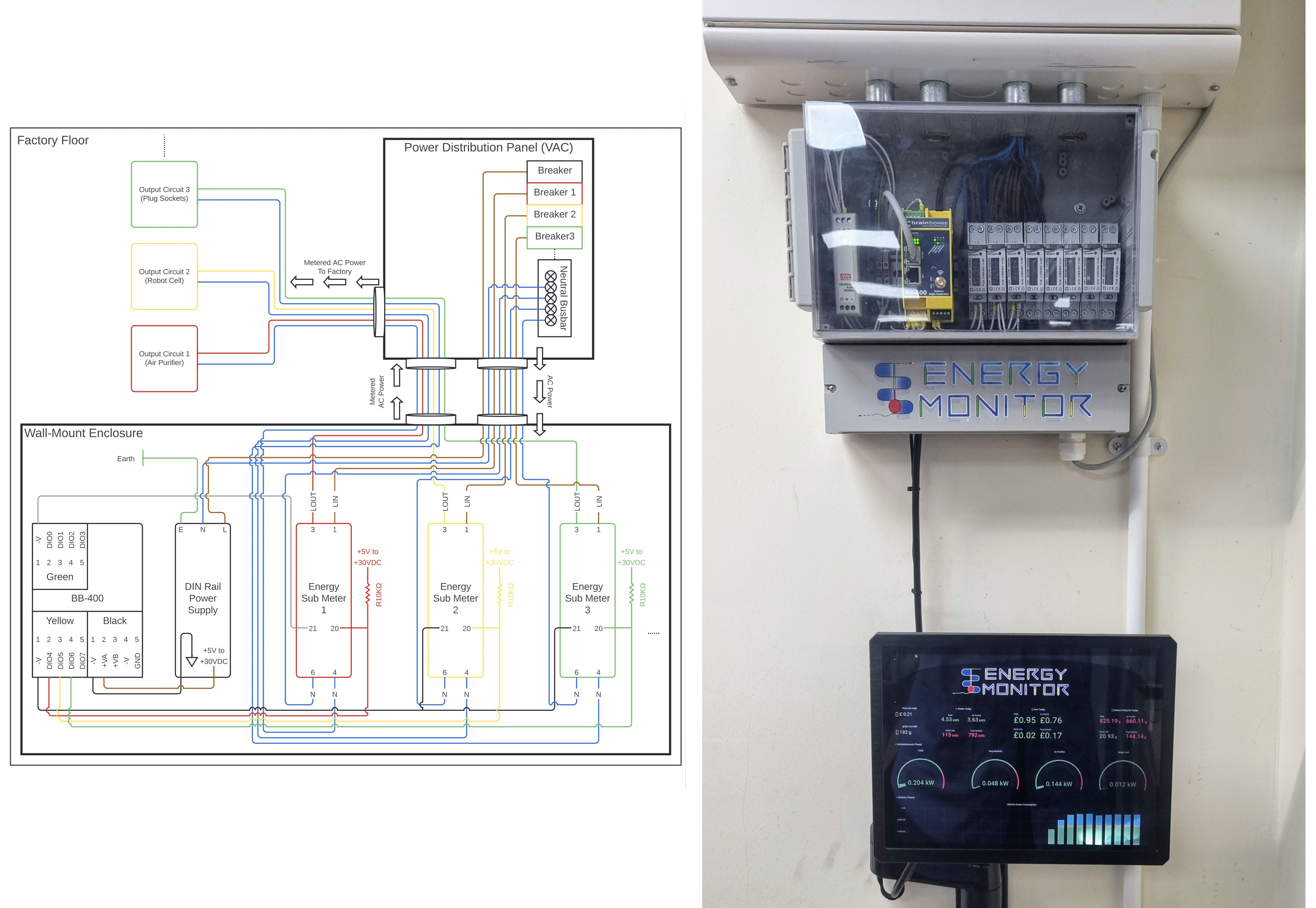
IIoT components in energy monitoring
IIoT energy monitoring involves several components, including sensors, gateways, communication protocols, cloud platforms, and analytics software.
Sensors: One of the critical components of IIoT in energy monitoring is sensors. These sensors are installed in various parts of the energy systems, such as transformers, circuit breakers, and generators. The sensors collect real-time data on energy consumption, voltage levels, and power quality. This data is then transmitted to a central system, which is then analyzed and used for energy management and optimization.

Edge computing: Another important IIoT component in energy monitoring is edge computing. Edge computing involves processing data at the network's edge, closer to where the data is generated. Edge computing will be essential for making allows for real-time analysis, decision-making, and changes. With edge computing, energy monitoring systems can detect anomalies, identify energy-saving opportunities, and trigger real-time alerts, improving energy systems' overall efficiency.
Cloud computing: This is also a crucial IIoT component in energy monitoring. Cloud computing allows storing and analyzing large volumes of data collected by sensors and other IIoT devices. With cloud computing, energy monitoring systems can provide real-time insights, trend analysis, and predictive maintenance, helping companies optimize their energy systems, reduce costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
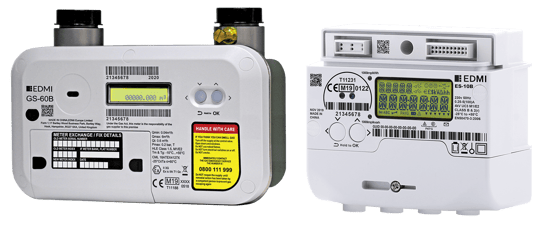
Smart meters and their role in IIoT energy monitoring
Smart meters are a critical component of IIoT energy monitoring. Smart meters are digital devices that measure energy consumption and wirelessly transmit data to the energy provider.
Smart meters enable businesses to track their energy usage in real time, allowing them to make informed decisions about it.
Smart meters also provide energy providers with real-time data about energy consumption, enabling them to manage the energy grid more efficiently. This helps to reduce energy waste, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
Predictive analytics in IIoT energy monitoring
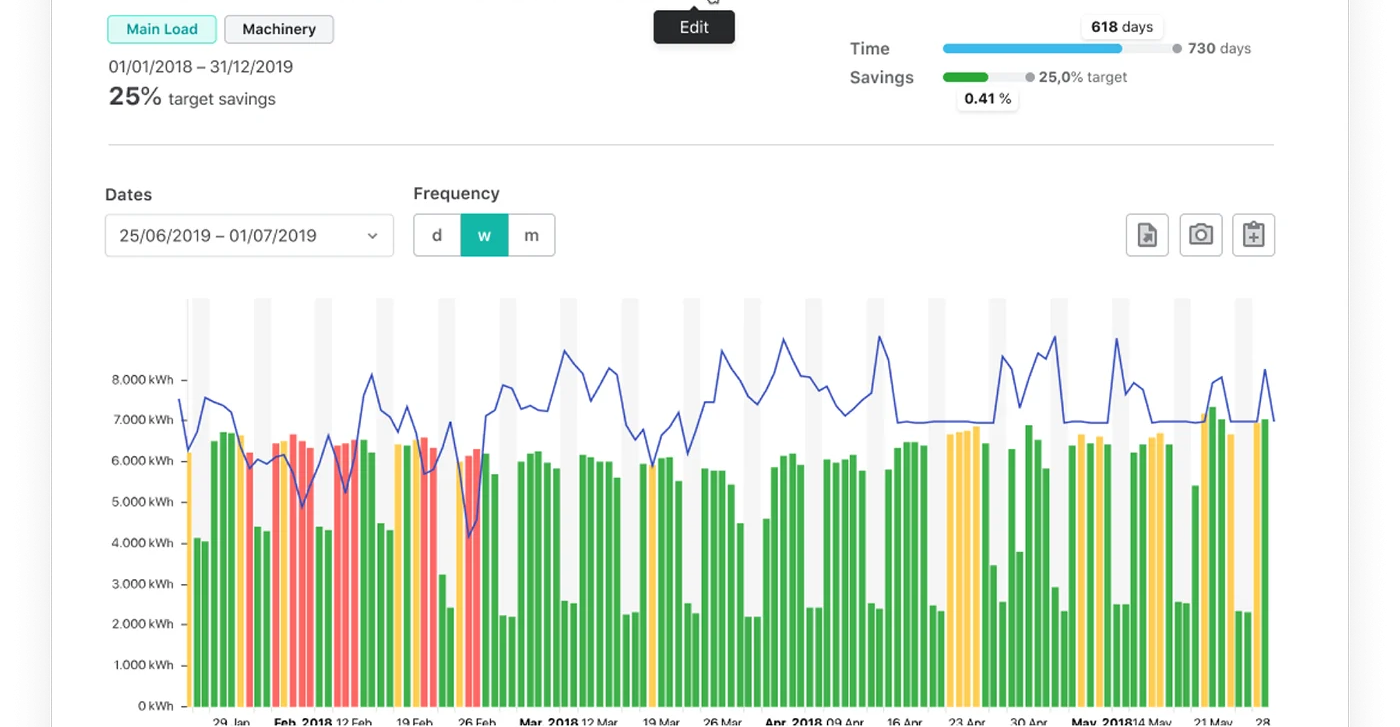
Predictive analytics has become an essential tool in the world of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) energy monitoring. This powerful technology allows companies to predict and prevent equipment failures, optimize energy usage, and improve efficiency. Advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques enable predictive analytics to analyze vast amounts of data and provide real-time insights into energy usage patterns. This information can help companies identify areas of inefficiency and take proactive measures to reduce energy waste and costs.
One of the main benefits of predictive analytics in IIoT energy monitoring is the ability to detect potential equipment failures before they occur. By monitoring equipment data in real-time, predictive analytics can identify patterns of behavior that indicate a potential problem. This information can alert maintenance teams to proactively prevent equipment failure, minimizing downtime and reducing repair costs. Additionally, predictive analytics can help companies optimize energy usage by analyzing data on energy consumption patterns. By identifying areas of excessive energy usage, companies can take steps to reduce energy waste and improve overall efficiency.
Another key advantage of predictive analytics in IIoT energy monitoring is the ability to forecast future energy demands. By analyzing historical data and usage patterns, predictive analytics can predict future energy needs, allowing companies to plan and allocate resources accordingly. Forecasting usage helps companies avoid unexpected energy demands and can enable companies to negotiate favorable utility rates and reduce energy costs.
Overall, predictive analytics is a valuable tool in IIoT energy monitoring. By providing real-time insights into energy usage patterns, predicting potential equipment failures, and forecasting future energy demands, companies can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and achieve sustainability goals.
Real-world examples of IIoT in energy monitoring
Several businesses have implemented IIoT in energy monitoring, achieving significant efficiency and cost savings benefits.
In the oil and gas industry, IIoT sensors are used to monitor the temperature and pressure of pipelines, reducing the risk of leaks and spills.
![]() In the renewable energy sector, IIoT devices monitor wind turbines and solar panels, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing downtime.
In the renewable energy sector, IIoT devices monitor wind turbines and solar panels, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing downtime.
Another example of IIoT in action is the manufacturing industry, where sensors monitor energy usage in real-time. Thus, it allows companies to identify areas where energy usage can be reduced, leading to cost savings and improved sustainability.
In the commercial sector, IIoT is being used to monitor and control HVAC systems, lighting, and other energy-consuming devices, leading to significant reductions in energy usage.
 In the transportation industry, IIoT sensors are used to monitor the fuel consumption of vehicles, allowing companies to optimize their fleet management and reduce fuel costs.
In the transportation industry, IIoT sensors are used to monitor the fuel consumption of vehicles, allowing companies to optimize their fleet management and reduce fuel costs.
In the mining industry, IIoT devices are used to monitor and control the energy usage of heavy machinery, leading to cost savings and improved safety.
Challenges of implementing IIoT in energy monitoring
While IIoT offers many benefits in energy monitoring, implementing it has several challenges. One of the significant challenges is the cost of deploying IIoT sensors and infrastructure. The price of sensors, gateways, and communication protocols can be high, making it difficult for businesses to justify the investment.
Another challenge is the complexity of integrating IIoT with existing energy monitoring systems. Many businesses already have legacy systems, which can be challenging to integrate with IIoT. In addition, legacy systems entail additional challenges and costs and usually take time to adopt and implement IIoT solutions.
Future of IIoT in energy monitoring
The future of IIoT in energy monitoring is bright, with many opportunities for innovation and growth. As the cost of sensors and infrastructure decreases, more businesses can implement IIoT in energy monitoring, achieving significant cost savings and efficiency improvements.
The future of IIoT in energy monitoring also involves the integration of other emerging technologies, such as blockchain and artificial intelligence. These technologies will enable businesses to track energy usage more accurately and securely, reducing costs and improving efficiency.