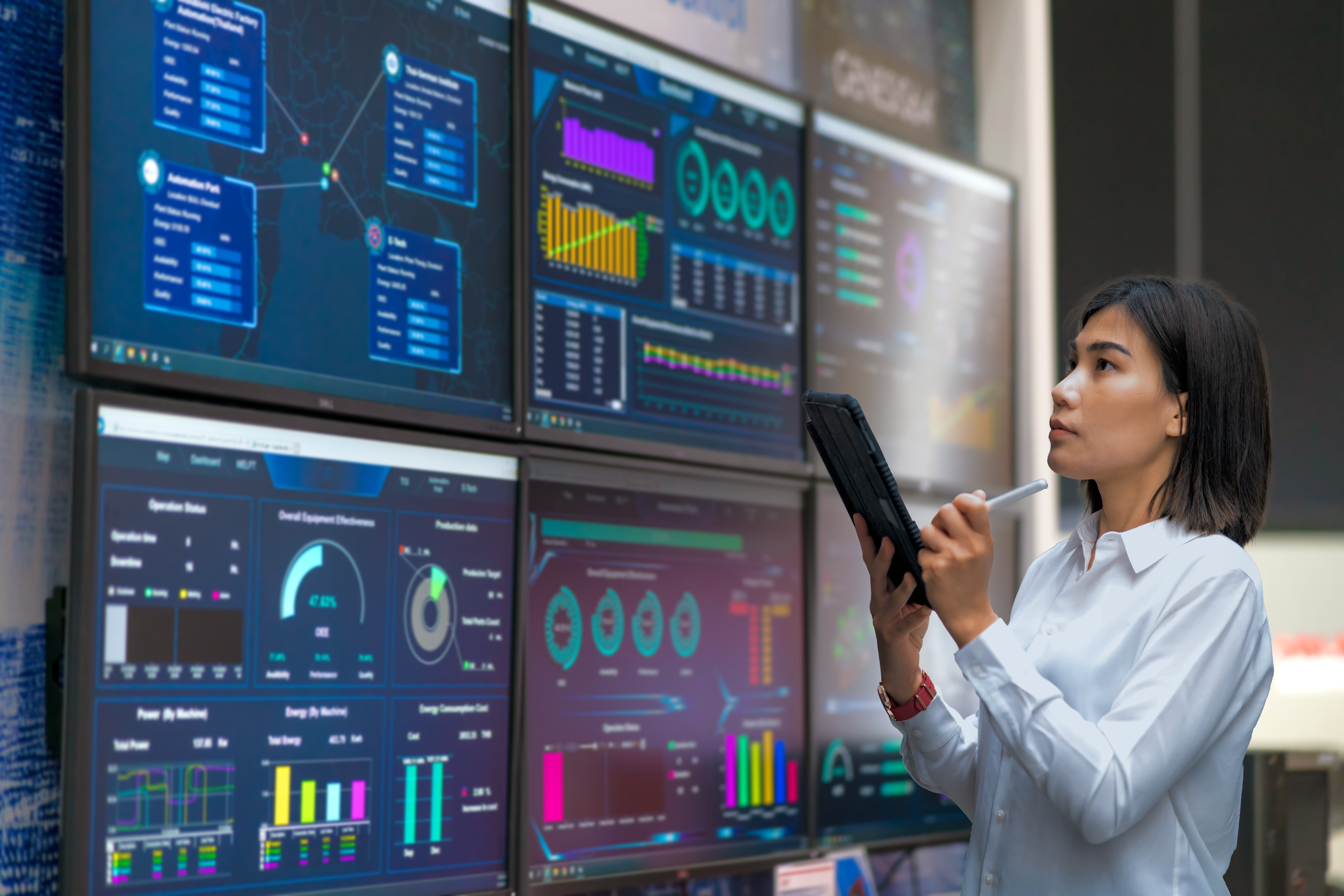
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has revolutionized industrial applications, opening new possibilities for connectivity and data-driven decision-making. By integrating sensors, devices, and software systems, IIoT enables real-time monitoring, automation, and optimization in various industries, ranging from manufacturing to energy.

IIoT holds immense potential for industrial applications, allowing companies to achieve higher productivity, efficiency, and safety. By harnessing the power of IIoT, organizations can gather vast amounts of data from their equipment, processes, and environments, enabling them to make informed decisions and take proactive actions. However, to fully leverage the benefits of IIoT, it is crucial to establish a robust alarm management system that can effectively handle the influx of data and provide timely notifications and insights.
Understanding the Importance of Alarm Management in Industrial Settings
In any industrial setting, alarm management is critical in ensuring personnel safety, protecting assets, and maintaining operational efficiency. Alarms serve as early warning systems, alerting operators to abnormal conditions or potential hazards that require immediate attention. Effective alarm management helps operators prioritize and respond to notices promptly, reducing the risk of accidents, equipment failures, and costly disruptions.
However, traditional alarm systems often suffer from many nuisance alarms, alarm floods, and alarm overload, leading to operator fatigue, desensitization, and missed critical alarms. These challenges can compromise the overall effectiveness of alarm management and hinder the ability to respond to emergencies promptly. Therefore, there is a growing need for an advanced alarm management system to address these challenges and enhance the efficiency and reliability of alarm handling processes.
Challenges Faced in Alarm Management and the Need for Advanced Systems
The complexity of modern industrial systems, coupled with the increasing amount of data generated by IIoT devices, poses significant challenges for alarm management. Traditional methods often need more capability to filter and prioritize alarms effectively, resulting in information overload for operators. This can lead to alarm fatigue, where operators become overwhelmed by the sheer volume of alarms and cannot respond adequately.
Moreover, the lack of contextual information and the inability to correlate alarms with underlying causes can make it easier for operators to identify the root causes of alarm activations. This hampers their ability to take proactive measures and prevent potential incidents from escalating. Additionally, the absence of predictive capabilities limits the ability to anticipate and address issues before they occur, leading to reactive rather than proactive alarm management.
An advanced alarm management system is required to overcome the challenges of operator and alarm incidents. Such a system should leverage the capabilities of IIoT to collect, analyze, and interpret data from various sources in real time. By integrating advanced analytics, machine learning, and predictive modeling, an advanced alarm management system can provide operators with actionable insights, enabling them to make informed decisions and respond proactively to alarms.

Key Components of an Advanced Alarm Management System
Building an advanced alarm management system involves several key components to ensure effective handling and response. These components include:
Data Acquisition and Integration:The first step in building an advanced alarm management system is establishing a robust data acquisition infrastructure. This involves deploying sensors, devices, and other data collection mechanisms to gather relevant information from the industrial environment. The collected data is then integrated with the alarm management system, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis.
Alarm Rationalization:Alarm rationalization is a critical process that involves reviewing and categorizing alarms based on their priority, severity, and relevance. By eliminating duplicate or unnecessary alarms and establishing clear alarm priorities, operators can focus on critical alarms and reduce the risk of missing important notifications.
Alarm Suppression and Shelving:An advanced alarm management system should incorporate alarm suppression and shelving capabilities to avoid alarm floods and minimize operator overload. This allows operators to temporarily suppress or shelve non-critical alarms during high activity or maintenance periods, ensuring they can focus on the most important warnings.
Alarm Visualization and Presentation:Presenting alarms clearly and intuitively is essential for effective alarm management. An advanced alarm management system should provide operators with a user-friendly interface that displays warnings in real-time, enabling quick identification and response. Visualizations such as color-coded alarms, trend charts, and geographical representations can enhance situational awareness and facilitate decision-making.
Alarm Analysis and Reporting:An advanced alarm management system should have built-in analytical capabilities to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in alarm data. By analyzing historical alarm data, operators can gain insights into recurring issues, identify potential bottlenecks, and implement proactive measures to prevent future incidents. Reporting functionalities can also provide comprehensive documentation of alarm events and performance metrics for regulatory compliance and continuous improvement.

Building a Robust IIoT Infrastructure for Alarm Management
Organizations must consider several key factors to build a robust IIoT infrastructure for alarm management. These include:
- Network Connectivity and Reliability:
A reliable network infrastructure is crucial for seamlessly transmitting alarm data between devices, sensors, and the central alarm management system. Redundancy and failover mechanisms should be implemented to ensure continuous connectivity and minimize the risk of data loss or disruption. - Data Security and Privacy:
As IIoT involves transmitting and storing sensitive data, organizations must prioritize data security and privacy. Implementing robust encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems can help safeguard critical information from unauthorized access or cyber threats. - Scalability and Flexibility:
The IIoT infrastructure should be designed to accommodate future expansions and changes in the industrial environment. Scalability and flexibility areessential to handle increasing data volumes, new devices, and evolving business requirements without compromising system performance or stability. - Integration with Existing Systems:
To maximize the value of IIoT, the alarm management system should seamlessly integrate with existing industrial control systems, data historians, and other relevant software applications. This enables data sharing, synchronization, and interoperability, allowing for a comprehensive view of the industrial processes and facilitating better decision-making. - Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance:
Once the IIoT infrastructure is in place, continuous monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure optimal performance. Regular inspections, software updates, and equipment maintenance should be conducted to identify and address potential issues or vulnerabilities that could impact the alarm management system.
Best Practices for Configuring and Optimizing Alarm Systems
Configuring and optimizing alarm systems is crucial to ensure their effectiveness and reliability. Here are some best practices to consider:
-
- Alarm Rationalization:
Conduct a thorough alarm rationalization process to eliminate unnecessary alarms, establish clear priorities, and define appropriate alarm limits and setpoints. Involving operators, engineers, and subject matter experts in this process can help ensure that the alarm system aligns with the operational requirements and reflects the criticality of different alarms. - Alarm Deadband and Hysteresis:
Setting appropriate deadbands and hysteresis for alarms can prevent unnecessary oscillations and reduce nuisance alarms. Deadband refers to the range within which a parameter must change before triggering a warning, while hysteresis defines the difference between the alarm activation and deactivation points. Fine-tuning these parameters based on process dynamics and control system characteristics can minimize false alarms and improve alarm system performance. - Alarm Shelving and Prioritization:
Implement alarm shelving capabilities to allow operators to temporarily suppress non-critical alarms during periods of high activity or maintenance. This helps reduce alarm floods and operator overload while ensuring that critical alarms are not missed. Establishing clear alarm priorities based on severity, safety, and operational impact enables operators to focus on alarms that require immediate attention. - Alarm Response Procedures:
Develop clear, well-documented alarm response procedures that outline the steps to be taken when specific alarms occur. These procedures should guide assessing the situation, verifying the alarm, and taking appropriate actions. Regular training and drills can help operators familiarize themselves with the processes and ensure a consistent and effective response. - Continuous Monitoring and Performance Evaluation:
Regularly monitor and evaluate the alarm system's performance to identify improvement areas. Analyze alarm data, operator response times, and alarm flood occurrences to gain insights into system performance and operator behavior. This feedback can guide further optimization efforts and help maintain the effectiveness of the alarm management system.
- Alarm Rationalization:
Implementing Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning for Proactive Alarm Management
Integrating predictive analytics and machine learning techniques into alarm management systems can significantly enhance their effectiveness and efficiency. By leveraging historical data, real-time sensor readings, and advanced algorithms, predictive analytics can identify patterns, anomalies, and potential alarm triggers. Machine learning algorithms can then be trained on this data to predict future alarms, detect emerging issues, and provide early warnings.
Predictive analytics and machine learning enable proactive alarm management by:
Early Detection of Anomalies
By analyzing historical data and detecting anomalies in sensor readings, predictive analytics can identify abnormal conditions that may lead to alarms. This allows operators to take preventive measures before alarms are triggered, minimizing the risk of incidents and disruptions.
Condition-Based Alarm Thresholds
Rather than relying on fixed alarm thresholds, machine learning algorithms can continuously adapt and optimize alarm limits based on real-time data and historical trends. This ensures that alarms are triggered at the appropriate thresholds, reducing false alarms and improving the accuracy of alarm notifications.
Root Cause Analysis
Machine learning algorithms can be trained to correlate alarms with underlying causes, helping operators identify the root causes of alarm activations. This enables them to address the underlying issues, preventing recurring alarms and improving system performance.
Proactive Maintenance and Optimization
Predictive analytics can identify patterns and trends in alarm data, enabling organizations to predict equipment failures, maintenance requirements, or performance degradation. Organizations can minimize downtime, extend equipment lifespan, and reduce costs by proactively scheduling maintenance activities and optimizing operational parameters.
By incorporating predictive analytics and machine learning into alarm management systems, organizations can transition from reactive to proactive alarm management, improving overall operational efficiency and reducing the risk of incidents.
Case Studies Showcasing Successful Implementations of Advanced Alarm Management Systems
To illustrate the benefits and capabilities of advanced alarm management systems, let's explore two case studies:
Case Study 1: 
Manufacturing Industry
A leading manufacturing company implemented an advanced alarm management system to address the challenges of alarm overload and operator fatigue. By rationalizing alarms and implementing alarm shelving capabilities, the company reduced the number of alarms per shift by 80%. The advanced system also provided real-time analytics and visualization tools, enabling operators to identify patterns and trends in alarm data. As a result, the company achieved a 30% improvement in overall equipment effectiveness and significantly reduced unplanned downtime.
Case Study 2:
Energy Sector
An energy company adopted an advanced alarm management system to enhance the safety and reliability of its power generation facilities. The company could detect early signs of equipment degradation and impending failures by integrating predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms. This proactive approach enabled timely maintenance interventions, preventing costly breakdowns and optimizing asset utilization. The advanced alarm management system also reduced the number of false alarms by 70%, allowing operators to focus on critical notices and respond more effectively to emergencies.
These case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits of advanced alarm management systems in industrial applications. By leveraging IIoT and incorporating advanced analytics, organizations can unlock the true potential of alarm management, leading to improved safety, efficiency, and productivity.
Future Trends and Advancements in IIoT-Based Alarm Management
The field of IIoT-based alarm management is continuously evolving, with several emerging trends and advancements on the horizon. Here are some future developments to watch out for:

- Edge Computing and Edge Analytics:
As IIoT devices become more powerful and capable, edge computing and edge analytics are expected to play a more significant role in alarm management. By processing data locally at the device level, edge computing reduces latency, enhances real-time responsiveness, and minimizes network bandwidth requirements. On the other hand, Edge analytics enables immediate data analysis and decision-making at the edge, reducing the need for centralized processing and improving overall system performance. - Integration with Artificial Intelligence:
Integrating IIoT-based alarm management systems with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies hold great potential for enhanced decision-making and automation. AI algorithms can analyze vast data, identify complex patterns, and make intelligent predictions or recommendations. Organizations can achieve more accurate alarm prioritization, automated response actions, and adaptive alarm limits by combining AI capabilities with alarm management systems. - Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality:
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies can transform operators' interaction with alarm management systems. AR overlays real-time alarm information onto the operator's field of view, providing contextual information and enhancing situational awareness. VR can create immersive virtual environments where operators can visualize alarms, simulate emergency scenarios, and practice response procedures. These technologies can improve operator effectiveness, training, and decision-making in alarm-intensive industrial settings. - Advanced-Data Analytics and Pattern Recognition:
As the volume of data generated by IIoT devices increases, advanced data analytics and pattern recognition techniques will become essential for effective alarm management. Machine learning algorithms can be trained on massive datasets to identify complex patterns, predict alarm triggers, and perform root cause analysis. Deep learning techniques, such as convolutional neural networks, can analyze visual data from cameras or thermal imaging sensors, enabling the detection of abnormal conditions or potential hazards.
Conclusion: Leveraging the Power of IIoT for Effective Alarm Management in Industrial Applications
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has the potential to revolutionize alarm management in industrial applications. Organizations can enhance safety, productivity, and operational efficiency by building an advanced alarm management system that leverages IIoT capabilities. The key components of such a system include data acquisition and integration, alarm rationalization, alarm suppression and shelving, alarm visualization and presentation, and alarm analysis and reporting.
To build a robust IIoT infrastructure for alarm management, organizations need to consider factors such as network connectivity, data security, scalability, and integration with existing systems. Best practices for configuring and optimizing alarm systems include alarm rationalization, alarm shelving and prioritization, defining alarm response procedures, and continuous monitoring and performance evaluation.
FAQ
Q1. What is the importance of alarm management in industrial settings?
A1. Alarm management is crucial in industrial settings as it ensures personnel safety, protects assets, and maintains operational efficiency. Alarms serve as early warning systems, alerting operators to abnormal conditions or potential hazards that require immediate attention. Effective alarm management helps prioritize and respond to notices promptly, reducing the risk of accidents, equipment failures, and costly disruptions.
Q2. What are the challenges in alarm management and the need for advanced systems?
A2. Traditional alarm systems often suffer from nuisance alarms, alarm floods, and alarm overload, leading to operator fatigue, desensitization, and missed critical alarms. The complexity of modern industrial systems, coupled with the increasing amount of data generated by IIoT devices, poses significant challenges for alarm management. An advanced alarm management system is needed to address these challenges and enhance efficiency and reliability by leveraging IIoT capabilities.
Q3. What are the key components of an advanced alarm management system?
A3. The key components of an advanced alarm management system include data acquisition and integration, alarm rationalization, alarm suppression and shelving, alarm visualization and presentation, and alarm analysis and reporting. These components work together to ensure effective handling and response to alarms, enabling operators to make informed decisions and take proactive actions.
Q4. How can organizations build a robust IIoT infrastructure for alarm management?
A4. To build a robust IIoT infrastructure for alarm management, organizations should consider factors such as network connectivity and reliability, data security and privacy, scalability and flexibility, and integration with existing systems. It is important to establish a reliable network infrastructure, prioritize data security, design for scalability, and ensure seamless integration with industrial control systems and relevant software applications.
Q5. What are the best practices for configuring and optimizing alarm systems?
A5. Some best practices for configuring and optimizing alarm systems include conducting thorough alarm rationalization to eliminate unnecessary alarms, setting appropriate deadbands and hysteresis to reduce false alarms, implementing alarm shelving and prioritization to manage high activity periods, developing clear alarm response procedures, and continuously monitoring and evaluating the alarm system's performance to identify improvement areas.