What is EMI?
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI), also known as radio-frequency interference (RFI), refers to the disturbance generated by external electrical sources having ill effects on the surrounding circuits. These disturbances are caused by electromagnetic radiation emitted from various electronic devices and can interfere with the operation of electronic equipment.
Which Devices are particularly prone to emitting EMI and causing electrical noise problems in Industrial Machinery? Here are the key culprits:
The rapid switching transients generate high-frequency noise that can radiate through power lines and induce noise in nearby circuits.
VFDs generate significant EMI due to their high-speed switching of power transistors, which can radiate through both conducted and radiated emissions.
Brushed DC motors, in particular, generate EMI from sparking at the commutator. Additionally, the rapid switching in motor controllers can create noise.
When switching, relays and contactors can produce arcing and high-frequency noise. The collapsing magnetic fields also generate transients.
Unshielded cables can pick up and radiate noise, especially in environments with high levels of electrical interference.
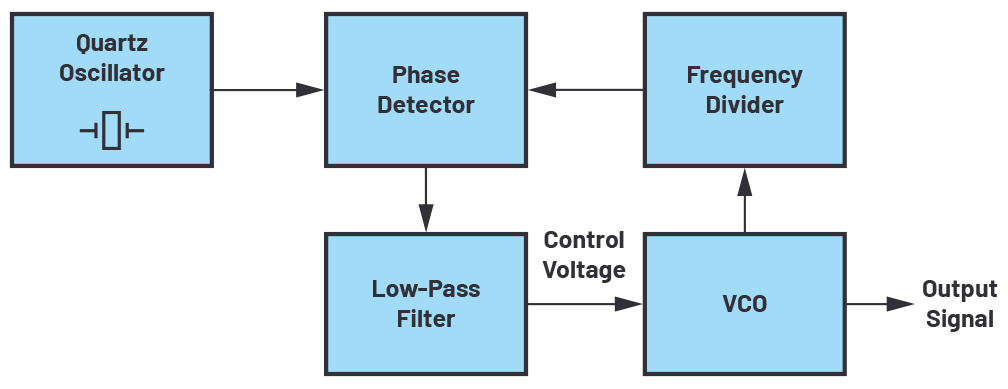
These are going to be found inside your "electronic" devices. oscillators generate high-frequency signals that can couple into other parts of the circuit and radiate EMI. Especially VCXO and oscillators that are designed with a PLL circuit.
These components often involve high-frequency switching to regulate power, leading to potential EMI issues.
The large currents involved in the process can create strong magnetic fields that can couple into other circuits, causing noise and interference.
Understanding these sources and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies can significantly reduce EMI-related problems in industrial machines.
-

EMC Cable Glands
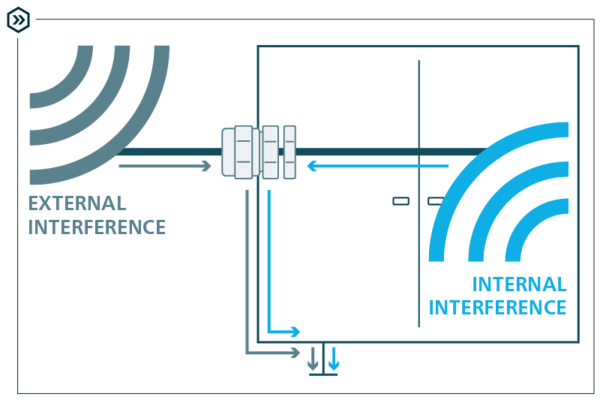
Reduces EMI: Provides a path for high-frequency noise to dissipate safely into the ground.
Prevents Ground Loops: Avoids the creation of loops that can pick up and amplify interference.
-

Shielding, Grounding, Cable Management
Shielding Clips & Seals: Conductive seals are used in enclosures to maintain shielding effectiveness when cables are passed through a bulkhead.
Equipotential Bonding: Connects metal parts to the same electrical potential to avoid differences that cause noise.
Physical Separation: Keeping power and signal cables apart to minimize the coupling of noise.
Routing: Running cables away from known EMI sources and avoiding parallel runs of power and signal lines.
Mitigation Strategies ...
- Shielding
- Filtering
- Proper Grounding
- Cable Management
- Component Selection
Shielding
Filtering
Using EMI filters on power lines and signal lines to attenuate high-frequency noise.
Proper Grounding
Ensuring all components are correctly grounded to provide a path for noise to dissipate.
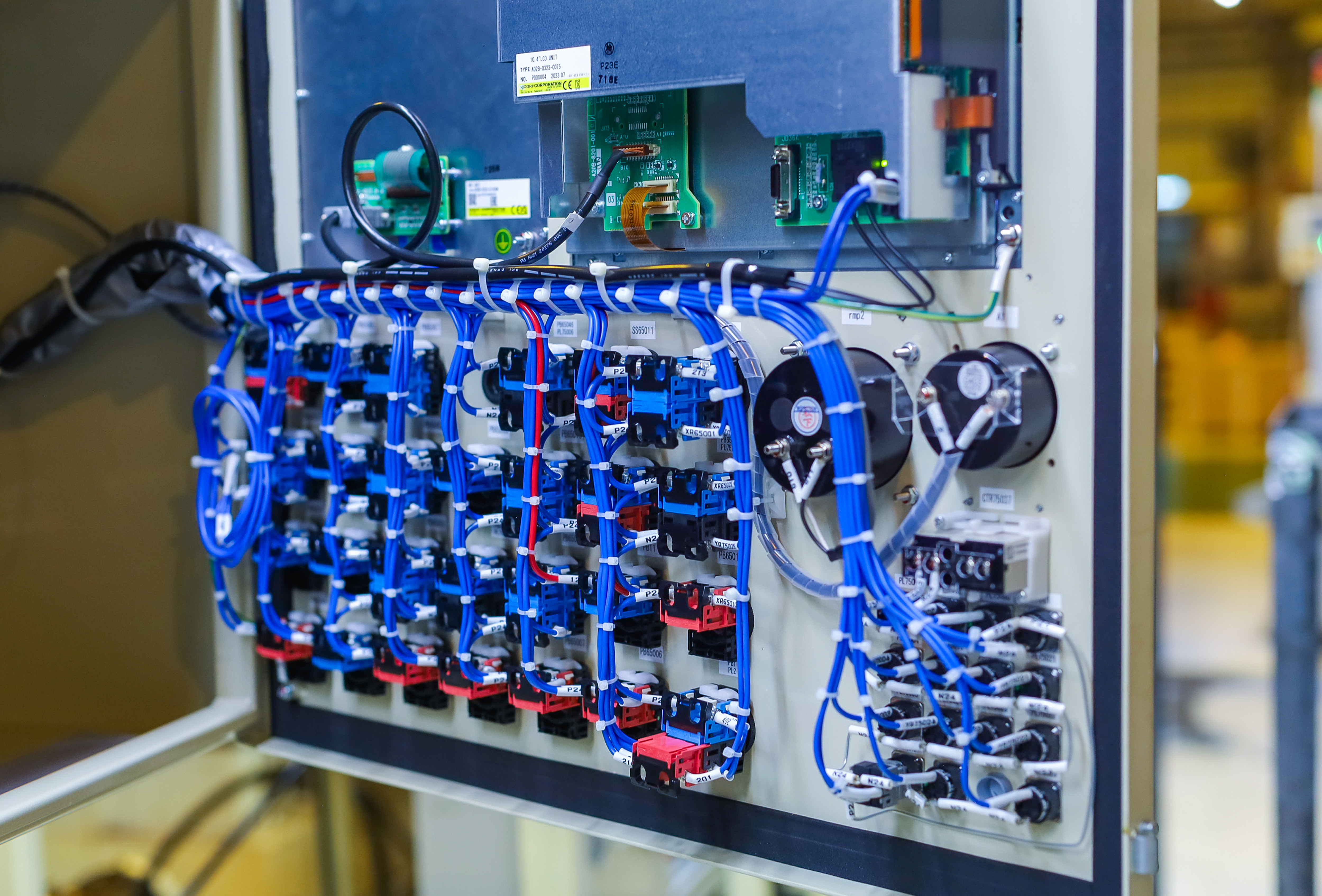
Cable Management

Component Selection
Technical Resources



Identifying and Addressing Industrial Machine EMC/EMI Issues: Expert Tips
-
Comprehensive Site Surveys:
- Conduct thorough surveys to identify potential EMI sources and vulnerable equipment.
- Use spectrum analyzers and other diagnostic tools to pinpoint frequencies and locations of EMI emissions.
-
Effective Shielding Techniques:
- Implement metallic enclosures around sensitive equipment to block external electromagnetic fields.
- Use shielded cables for signal and power lines to prevent EMI from coupling into or out of the cables.
-
Optimal Grounding Practices:
- Ensure proper grounding of all equipment to provide a path for EMI to dissipate.
- Single-Point Grounding: Use a single grounding point to avoid ground loops, which can create potential differences and noise.
- Equipotential Bonding: Connect all metal parts of the machinery and enclosures to a common ground to ensure they are at the same electrical potential.
- Grounding of Shields: Ground the shields of cables at one end to avoid creating loops but ensure that they are effectively connected to the ground at that point.
-
Proper Cable Management:
- Separate power and signal cables to minimize the risk of coupling noise.
- Route cables away from known EMI sources and use twisted pair cables to cancel out noise.
- Use EMC Cable Glands:
- EMC cable glands are designed to provide a secure connection while maintaining the electromagnetic integrity of the enclosure and shielding the cable.
- EMC cable glands are designed to provide a secure connection while maintaining the electromagnetic integrity of the enclosure and shielding the cable.
-
Component Selection and Layout:
- Choose components with lower EMI emissions and better inherent filtering capabilities.
- Optimize the layout of electronic devices, minimize potential ground loop areas, pay attention to wich devices have a high potential for radiated emissions.
-
Use of Suppression Devices:
- Employ transient voltage suppressors (TVS) and metal-oxide varistors (MOVs) to protect against voltage spikes.
- Install snubber circuits across inductive loads to suppress switching transients.
-
Filtering Solutions:
- Install EMI filters on power supply lines to attenuate high-frequency noise.
- Use ferrite beads and common-mode chokes on signal lines to reduce conducted EMI.
-
Regular Maintenance and Inspection:
- Perform regular maintenance on all equipment to ensure shielding and grounding remain effective.
- Inspect connectors and cables for wear and degradation that could compromise EMI mitigation measures.
-
Training and Awareness:
- Educate staff on the importance of EMC/EMI practices and proper handling of equipment.
- Stay updated with the latest standards and guidelines for EMI mitigation.
-
Simulation and Testing:
- Use simulation tools to predict EMI behavior and identify potential issues during the design phase.
- Conduct pre-compliance testing to ensure equipment meets EMC standards before deployment.