Machine safety is a critical aspect of any industrial operation. With the increasing use of automation and robotics in the manufacturing sector, the need to ensure the safety of both workers and equipment has become paramount. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of machine safety, including the importance of safety measures, the role of risk assessments, and how to implement adequate safety systems. By the end of this blog, you will thoroughly understand the different components that contribute to a safe and productive work environment.
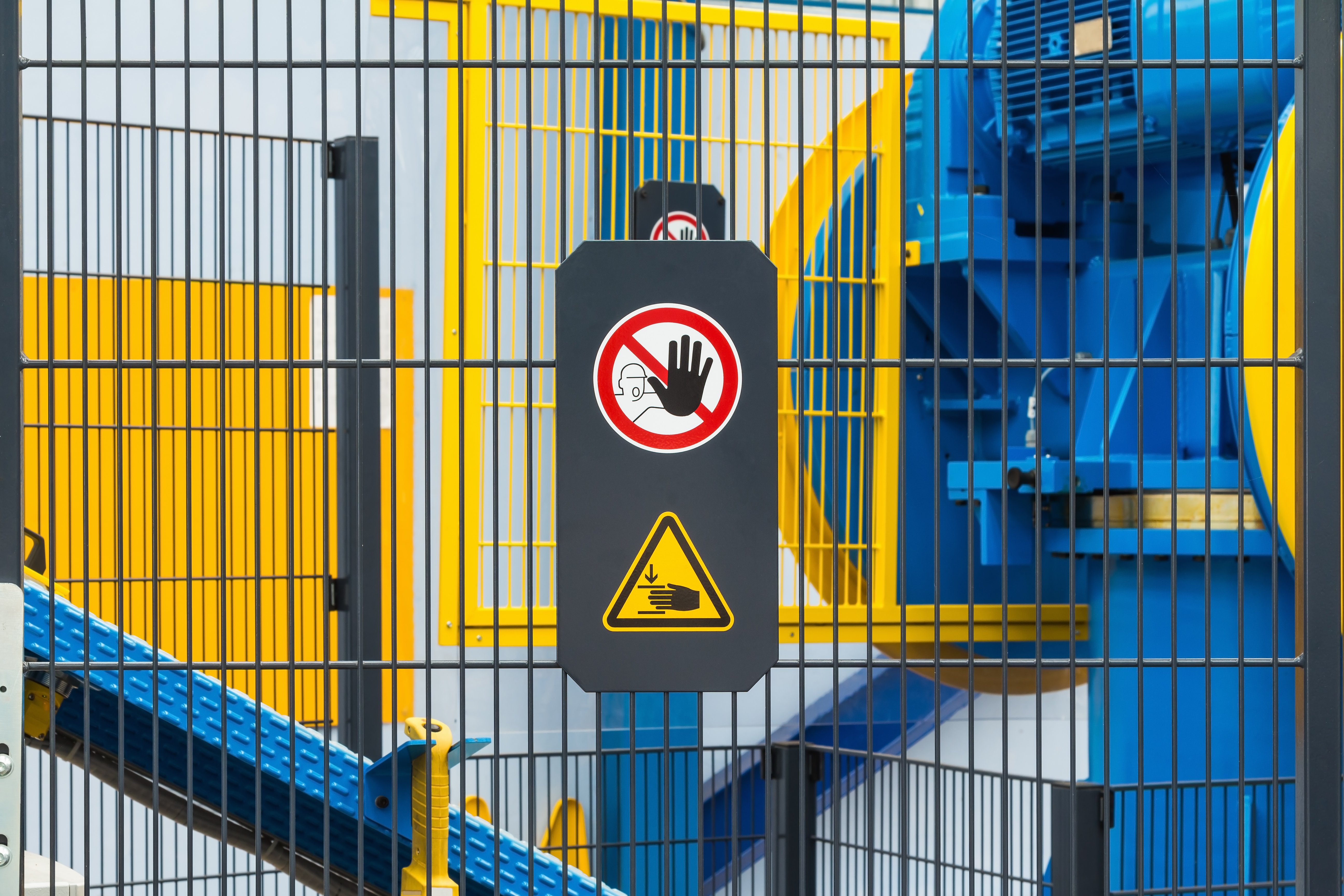

Importance of Machine Safety
Machine safety is essential for various reasons, including protecting workers, preventing costly equipment damage, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Below are some key factors that highlight the significance of machine safety in the workplace.
Protecting Workers
The primary reason for implementing machine safety measures is to protect employees from potential injuries and fatalities. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, nearly 2.8 million nonfatal workplace injuries and illnesses were reported by private industry employers in 2019. By implementing adequate safety measures, companies can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents and ensure a safer work environment for their employees.
Preventing Equipment Damage
In addition to protecting workers, machine safety measures help prevent costly equipment damage. Industrial machinery can be expensive to repair or replace; damage to these machines can lead to significant downtime and lost productivity. By implementing proper safety measures, companies can minimize the risk of equipment damage and reduce the associated costs.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with safety regulations is another crucial aspect of machine safety. Many countries have established strict safety regulations for industrial operations, and failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, penalties, and even shutdowns of operations. By implementing adequate safety measures, companies can ensure compliance with these regulations and avoid the negative consequences of non-compliance.
Risk Assessment: Identifying Potential Hazards
A comprehensive risk assessment is crucial in developing a practical machine safety strategy. This process involves identifying potential hazards associated with each machine and evaluating the likelihood and severity of accidents resulting from these hazards.

Steps in Conducting a Risk Assessment
- Identify potential hazards: This step involves examining each machine and identifying threats such as moving parts and electrical and ergonomic risks. It is essential to consider all possible sources of danger, including those that may arise from human error or machine malfunction.
- Evaluate the risks: Once potential hazards have been identified, the next step is to assess the likelihood and severity of accidents resulting from these hazards. This evaluation should consider factors such as the frequency of exposure to the risk, the effectiveness of existing safety measures, and the potential consequences of an accident.
- Prioritize risks: Based on the evaluation, risks should be prioritized according to their potential impact on worker safety and business operations. This prioritization will help guide the development of appropriate safety measures and controls.
- Implement safety measures: Once the risks have been prioritized, appropriate safety measures should be implemented to mitigate the identified hazards. These measures may include engineering controls, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Monitor and review: The final step in the risk assessment process is to monitor and review the effectiveness of the implemented safety measures. This ongoing process ensures that the safety measures remain effective and allows for adjustments as needed.
Engineering Controls: Designing Safety into Machines
Engineering controls are physical modifications or designs that eliminate or reduce potential hazards. These controls can be built into the machine during the design phase or added later as retrofits. Some examples of engineering controls include:
Machine Guarding
Machine guarding uses barriers or shields to protect workers from moving parts, sparks, and other hazards. Standard machine guards include fixed guards, adjustable guards, and self-adjusting guards. These guards should be designed to prevent unauthorized access to hazardous areas while allowing for proper machine operation and maintenance.
Safety Interlocks
Safety interlocks prevent the machine from operating unless certain safety conditions are met. For example, an interlock may prevent a machine from starting unless all the guards are in place, or it may stop the machine if a worker enters a hazardous area. Interlocks can be mechanical, electrical, or electronic and should be designed to prevent bypassing or tampering.

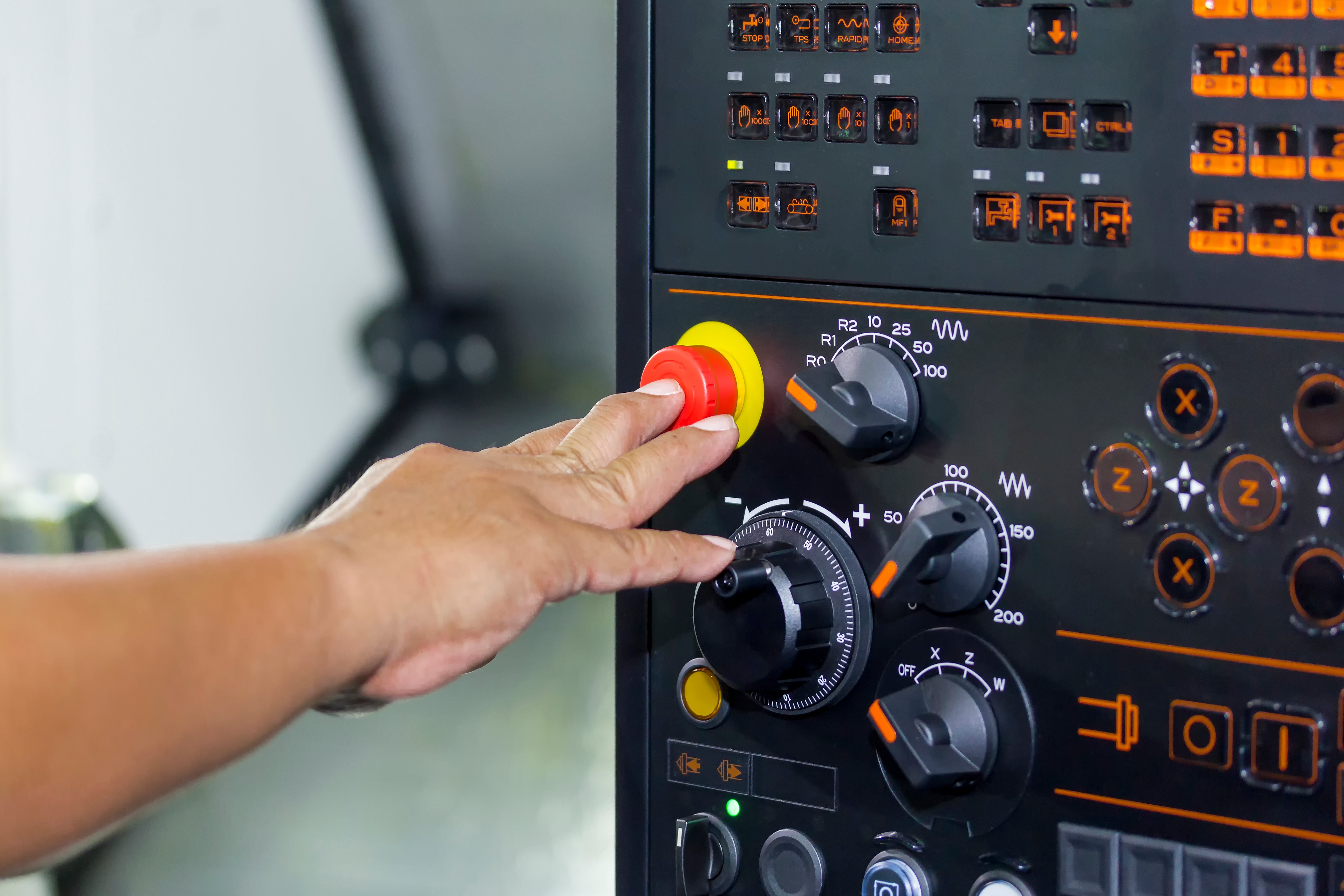
Emergency Stop Devices
Emergency stop devices are controls that allow workers to quickly and easily stop a machine in an emergency. These devices should be clearly labeled, easily accessible, and designed to prevent the machine as soon as possible without creating additional hazards.

Administrative Controls: Implementing Safety Procedures and Training
Administrative controls are policies, procedures, and training programs that help reduce the risk of accidents by promoting safe work practices. Some examples of administrative controls include:
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
SOPs are written instructions that outline the correct procedures for operating and maintaining machines. These procedures should be clear, concise, and accessible to all workers. Regular reviews and updates of SOPs are essential to ensure they remain adequate and relevant.
Training Programs
Proper training ensures workers understand the risks associated with their jobs and know how to operate machines safely. Training programs should cover topics such as hazard identification, safe operating procedures, and the use of PPE. Refresher training should be conducted periodically to ensure that workers remain aware of safety procedures and any changes that may have been made.
Lockout/Tagout Procedures
During maintenance and repair, lockout/tagout procedures ensure that machines are properly shut down and isolated from energy sources. These procedures help prevent the accidental startup of machines, which can lead to severe accidents and injuries.

Personal Protective Equipment: Providing the Last Line of Defense
Workers wear PPE to protect against hazards and minimize the risk of injury. PPE should be considered the last line of defense, as it does not eliminate hazards but provides protection when other safety measures fail or are not feasible. Examples of PPE used in industrial settings include safety goggles, gloves, earplugs, and steel-toed boots.
Selecting the Right PPE
When selecting PPE, it is essential to consider the specific hazards associated with each job and choose equipment that provides adequate protection without hindering the worker's ability to perform their tasks. It is also crucial to ensure that PPE fits properly and is comfortable to wear, as ill-fitting or uncomfortable equipment may not provide the desired level of protection.
Training Workers on the Proper Use of PPE
Workers must be trained on the proper use, care, and maintenance of PPE. This training should cover topics such as how to put on and take off the equipment, inspect the equipment for signs of wear or damage, and clean and store the equipment properly.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Regular maintenance and inspections ensure that machines operate safely and efficiently. Some critical aspects of a successful care and inspection program include:

Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance involves performing regular service and upkeep on machines to prevent breakdowns and extend their useful life. This may include lubricating moving parts, replacing worn components, and cleaning filters. A well-planned preventive maintenance program can help prevent unexpected equipment failures and minimize downtime.
Routine Inspections
Routine inspections involve visually checking machines for signs of wear, damage, or potential hazards. Training personnel should conduct these inspections and cover areas such as machine guarding, safety interlocks, and emergency stop devices. Any issues identified during the review should be addressed promptly to prevent accidents and ensure safe operation.
Recordkeeping
Keeping accurate records of maintenance and inspection activities is essential for tracking the performance of machines and identifying trends or patterns that may indicate potential problems. These records can also demonstrate compliance with safety regulations and provide valuable information for future risk assessments and safety planning.
Involving Workers in Machine Safety
Worker involvement is a crucial component of a successful machine safety program. By actively involving workers in developing and implementing safety measures, companies can benefit from their knowledge and expertise and create a more robust safety culture. Some ways to involve workers in machine safety include:
Encouraging Reporting of Hazards
Workers should be encouraged to report any hazards or safety concerns they encounter. This reporting can be done through formal channels such as safety committees or informal methods such as suggestion boxes or one-on-one conversations with supervisors.
Involving Workers in Risk Assessments and Safety Planning
Involving workers in the risk assessment process can help identify potential hazards that may have been overlooked and provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of existing safety measures. Workers can also play a vital role in developing safety plans, as they are often the ones who will implement the safety measures and can provide input on what will be most effective and practical.
Providing Opportunities for Safety Training and Education
Providing workers with safety training and education can increase their awareness of potential hazards and improve their ability to identify and address safety issues. Training may include:
- Formal training programs.
- Safety seminars and workshops.
- Access to safety resources such as articles and videos.
Integrating Machine Safety with Overall Safety Management
In collaboration with others, machine safety should be considered an integral part of a company's overall safety management system. This integrated approach helps ensure that all safety aspects are considered and addressed in a coordinated and cohesive manner. Some critical elements of an integrated safety management system include:
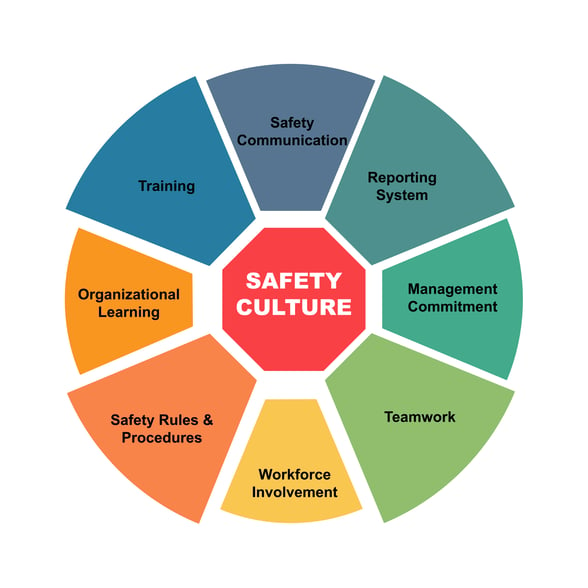
A Strong Safety Culture
A strong safety culture is one in which safety is a core value and a shared responsibility among all employees. This culture is built through leadership commitment, open communication, and a focus on continuous improvement.
Comprehensive Safety Policies and Procedures
An effective safety management system includes comprehensive safety policies and procedures that address all safety aspects, including machine safety, workplace ergonomics, and emergency response. These policies and procedures should be regularly reviewed and updated to remain effective and relevant.
Regular Audits and Reviews
Regular audits and reviews of safety performance help identify areas for improvement and ensure that safety measures remain effective. These audits can be conducted internally or by third-party organizations and should cover all aspects of the safety management system, including machine safety.
The Role of Technology in Machine Safety
Technological advancements are increasingly crucial in machine safety, with new devices and systems offering enhanced protection and improved efficiency. Some examples of these technologies include:

Advanced Sensors
Advanced sensors can monitor various aspects of machine operation, such as temperature, pressure, and vibration. These sensors can help detect problems before they become serious, allowing for timely intervention and maintenance.
Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation can help improve machine safety by reducing the need for workers to interact with hazardous machinery. By automating specific tasks, companies can minimize the risk of injury and ensure a safer work environment.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine Safety
The IoT is a network of interconnected devices communicating and sharing data. IoT devices can monitor machine performance and detect potential hazards in machine safety in real-time. This information can then be used to inform maintenance and safety measures decisions.
Conclusion
Machine safety is a critical aspect of ensuring a safe and productive workplace. By understanding the importance of machine safety, conducting thorough risk assessments, and implementing effective safety measures, companies can protect their workers, prevent equipment damage, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Industrial safety starts with safe machines and an overall safety management program. By embracing new technologies businesses can create a safer work environment and continuously improve their safety performance.