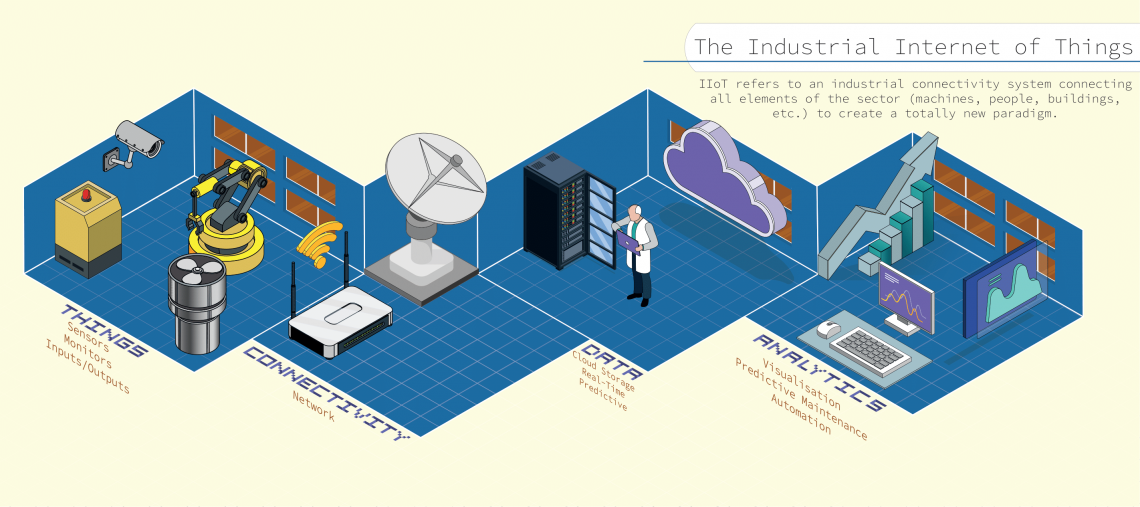
Proximity sensors are becoming increasingly popular in various industries due to their ability to detect the presence of objects without physical contact. They are used in multiple applications, from manufacturing and automotive to food processing and packaging. This blog aims to provide an in-depth look at the different types of proximity sensors, their applications, advantages, and so much more.
Introduction to Proximity Sensors
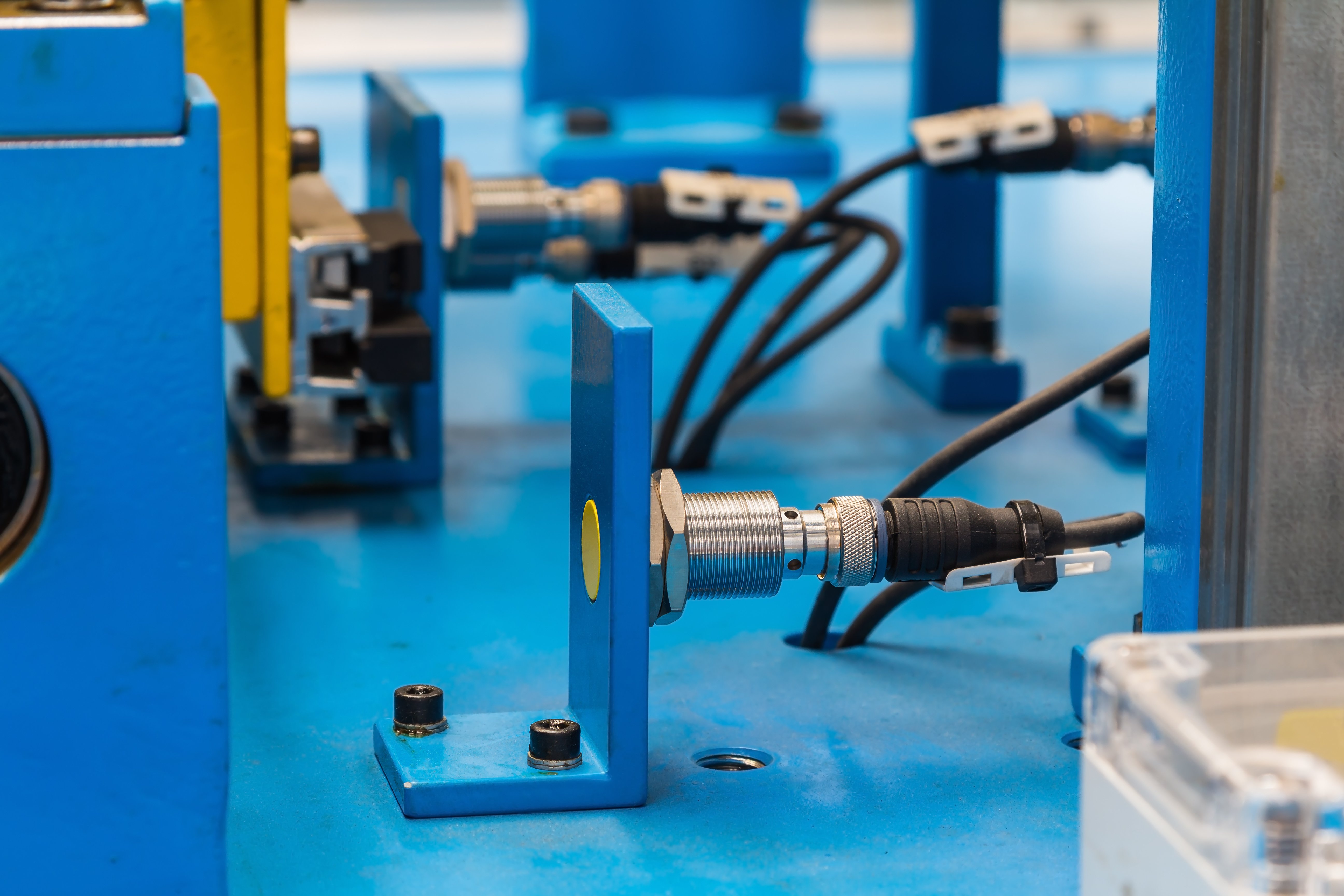
Proximity sensors are devices that detect the presence of an object without physical contact. They emit a signal and measure the distance between the sensor and the object. The signal can be in the form of light, sound waves, or magnetic fields, depending on the type of sensor.
Proximity sensors are used in various applications, from automotive and manufacturing to food processing and packaging. They are also used in security systems and consumer electronics, such as smartphones and tablets.
Types of Proximity Sensors
There are different types of proximity sensors, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types are inductive, capacitive, ultrasonic, magnetic, and photoelectric sensors.
- Inductive Proximity Sensors
Inductive proximity sensors detect metallic objects by measuring changes in magnetic fields. They are commonly used in manufacturing and automotive applications, such as detecting the presence of metal components on an assembly line.
Inductive sensors have an extended sensing range and are resistant to harsh environments. However, they are unsuitable for non-metallic objects and can be affected by electromagnetic interference.
- Capacitive Proximity Sensors
Capacitive proximity sensors detect objects by measuring changes in an electric field. They are commonly used in food processing and packaging applications, such as detecting the presence of liquids or powders.
Capacitive sensors are sensitive to non-metallic objects and have a long sensing range. However, they can be affected by temperature changes and humidity.
- Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors
Ultrasonic proximity sensors use sound waves to detect objects. They are commonly used in automotive applications, such as parking sensors and collision avoidance systems.
Ultrasonic sensors have a long sensing range and are not affected by color or transparency. However, they can be affected by temperature changes and can be affected by ambient noise.
- Magnetic Proximity Sensors
Magnetic proximity sensors detect magnetic fields and are commonly used in security systems and consumer electronics, such as smartphones and tablets.
Magnetic sensors have a long sensing range and are unaffected by temperature changes or humidity. However, they are sensitive to metallic objects and can be affected by electromagnetic interference.
- Photoelectric Proximity Sensors
Photoelectric proximity sensors use light to detect objects and are commonly used in packaging and material handling applications, such as detecting the presence of boxes on a conveyor belt.
Photoelectric sensors have a long sensing range and are unaffected by temperature changes or humidity. However, they can be affected by ambient light and can be sensitive to color and transparency.
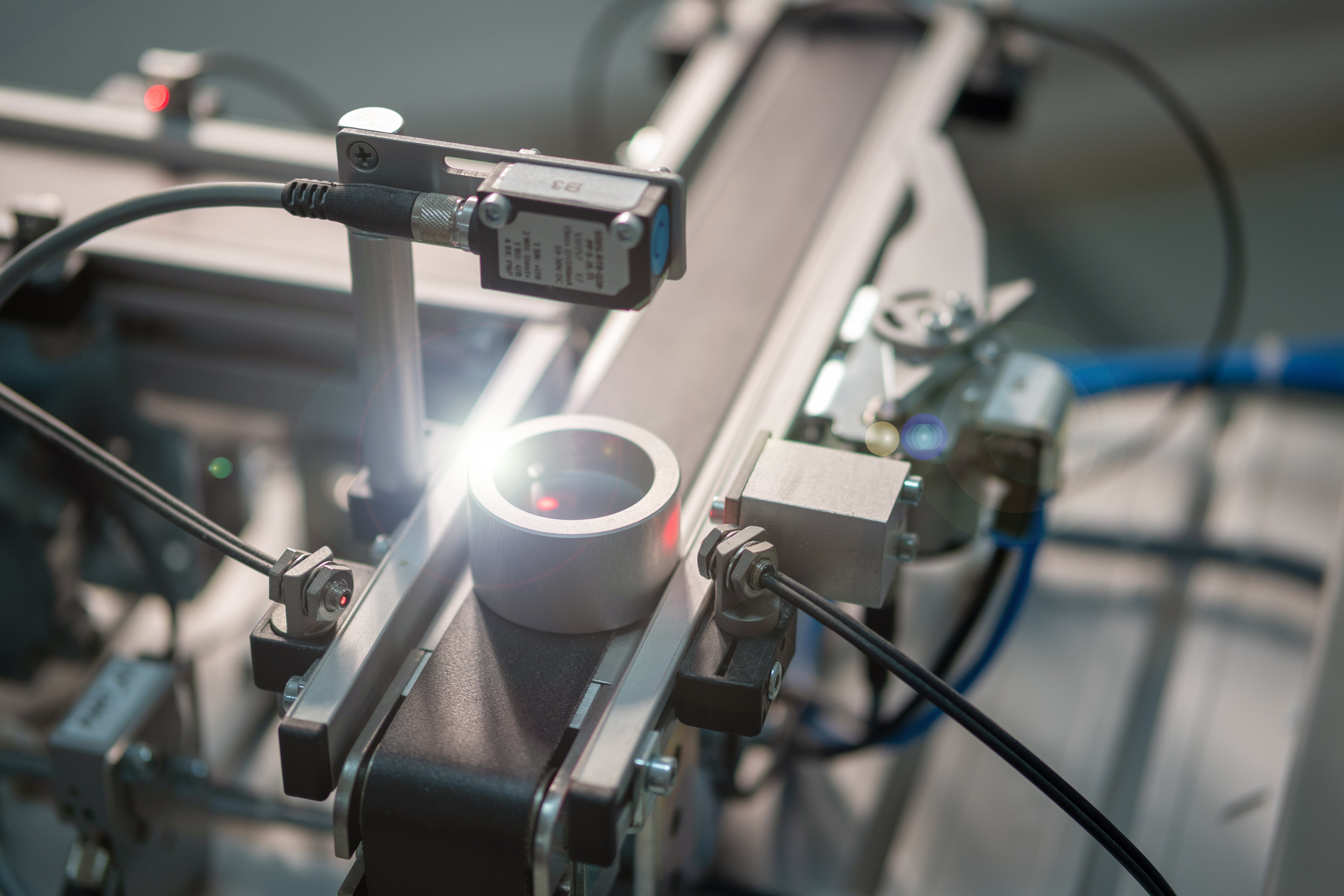
Applications of Proximity Sensors in Various Industries
Proximity sensors are used in a wide range of industries, from automotive and manufacturing to food and beverage. They are used to improve safety, increase efficiency, and reduce downtime.
- Automotive Industry
Proximity sensors are used in the automotive industry for various applications, such as parking sensors, collision avoidance systems, and automatic braking systems. They are also used to detect the presence of passengers and adjust airbag deployment accordingly.
- Manufacturing Industry
Proximity sensors are used in the manufacturing industry for a variety of applications, such as detecting the presence of components on an assembly line, monitoring machine performance, and detecting safety hazards.
- Food and Beverage Industry
Proximity sensors are used in the food and beverage industry for many applications, such as detecting the presence of liquids or powders, monitoring food quality, and ensuring packaging integrity.
- Other Industries
Proximity sensors are also used in other industries, such as construction, mining, and aerospace, for various applications, such as detecting the presence of obstacles and monitoring structural integrity.
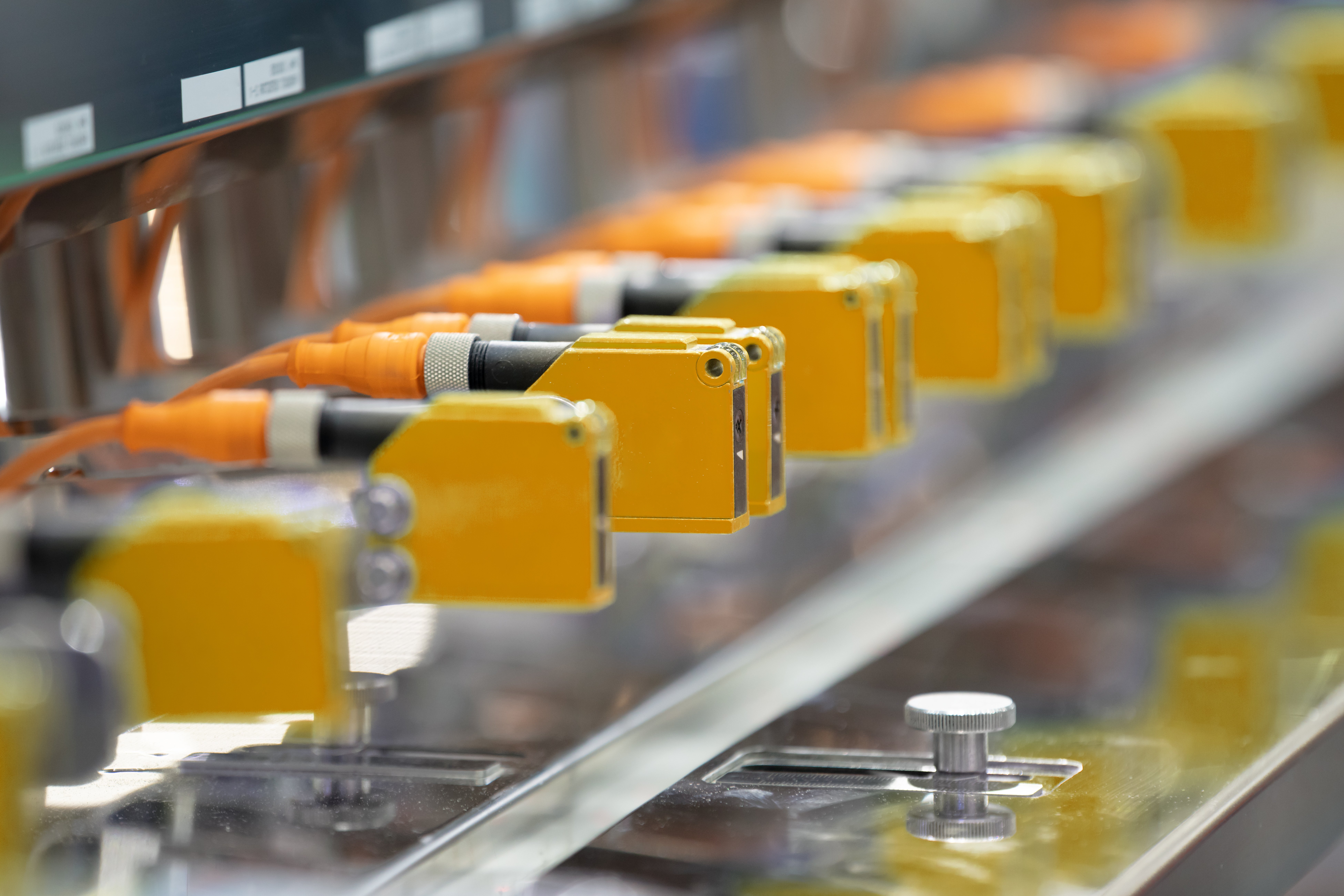

Advantages of Using Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors offer several advantages over other types of sensors. These advantages include:
-
- Non-contact Sensing
Proximity sensors can detect the presence of objects without physical contact, reducing wear and tear on equipment and minimizing the risk of damage.
-
- High Precision
Proximity sensors can detect objects with high precision, making them ideal for applications that require accurate positioning and control.
-
- Fast Response Time
Proximity sensors can detect objects quickly, making them ideal for applications that require fast response times.
-
- Easy to Use
Proximity sensors are easy to install and use, requiring little or no maintenance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Proximity Sensor
When choosing a proximity sensor, there are several factors to consider, including:
-
- Sensing Range
The sensing range of a proximity sensor determines how far it can detect objects. Choosing a sensor with a sensing range that is appropriate for the application is essential.
-
- Sensing Method
Different types of proximity sensors use different sensing methods, such as electromagnetic, ultrasonic, or optical. Choosing a sensor with a sensing method appropriate for the application is crucial.
-
- Environmental Conditions
Proximity sensors can operate in a wide range of temperatures and environments, but choosing a sensor appropriate for the application's specific environmental conditions is vital.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors require little or no maintenance, but some steps can be taken to ensure their continued operation. These steps include:
-
- Regular Cleaning
Proximity sensors should be cleaned regularly to remove dust and debris that can interfere with their operation.
-
- Calibration
Proximity sensors should be calibrated regularly to ensure accurate operation.
-
- Troubleshooting
If a proximity sensor fails to operate correctly, it is important to troubleshoot the problem to determine the cause and take appropriate action.
Future Trends in Proximity Sensor Technology
Proximity sensor technology is evolving rapidly, with new sensors being developed that offer improved performance and capabilities. Some of the future trends in proximity sensor technology include:
- Miniaturization
Proximity sensors are becoming smaller and more compact, making them ideal for limited-space applications.
- Wireless Connectivity
Proximity sensors are being developed with wireless connectivity, allowing them to communicate with other devices and systems.
- Smart Sensors
Proximity sensors are being developed with advanced features like self-diagnosis and predictive maintenance.
Proximity Sensors: Comparison
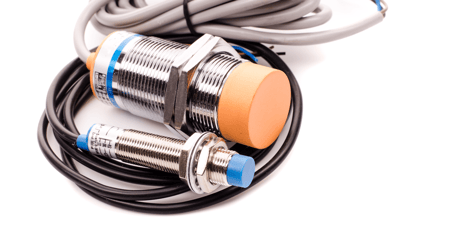
Each sensor type has advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for different applications.
- Inductive sensors use electromagnetic fields to detect metal objects. They are durable, reliable, and can operate in harsh environments. However, they have limitations in detecting non-metallic materials.
- Capacitive sensors detect the presence of any object that has a dielectric constant more significant than that of air. They are highly sensitive and can detect small changes in capacitance. However, they are unsuitable for detecting metal objects and may be affected by environmental factors such as humidity.
- Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to detect objects. They can detect a wide range of materials, including transparent or opaque objects. They are also resistant to dust and dirt. However, they may have difficulties detecting small things and may be affected by temperature changes.
- Photoelectric sensors use light to detect objects. They can detect a variety of materials, including transparent or opaque objects. They are also fast and accurate. However, they may be affected by ambient light and may have difficulties detecting shiny or reflective objects.
- Magnetic sensors use magnetic fields to detect metal objects. They can operate in harsh environments and are resistant to dust and dirt. However, they have limitations in detecting non-metallic materials and may be affected by other magnetic fields.
In conclusion, the choice of proximity sensor depends on the specific application requirements. It is crucial to consider the advantages and disadvantages of each type of sensor before making a decision.
Conclusion
Proximity sensors are revolutionizing various industries by improving safety, increasing efficiency, and reducing downtime. There are different types of proximity sensors, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. When choosing a proximity sensor, it is crucial to consider factors such as sensing range, resolution, accuracy, and the operating environment.
Proximity sensors require regular maintenance to ensure they continue to operate correctly. Troubleshooting common problems can also help to prevent downtime and reduce maintenance costs.
As proximity sensor technology continues to evolve, new sensors are being developed to meet the demands of various industries. Proximity sensors offer several advantages over other types of sensors, but they are only suitable for some applications.